Heat decarbonisation plays a vital role in achieving net zero. Find out more about what it is and why it’s beneficial in our latest blog.
The climate crisis continues to be at the forefront of the international agenda – and while we still have a long way to go on our journey towards net zero, positive steps and conversations are moving us closer to that target. One of those steps is heat decarbonisation.
Heat decarbonisation – the process of reducing greenhouse gas emissions associated with heating – is gaining traction. Here we take a closer look at what it is and how it will play a key role in net zero emissions.
What is heat decarbonisation?
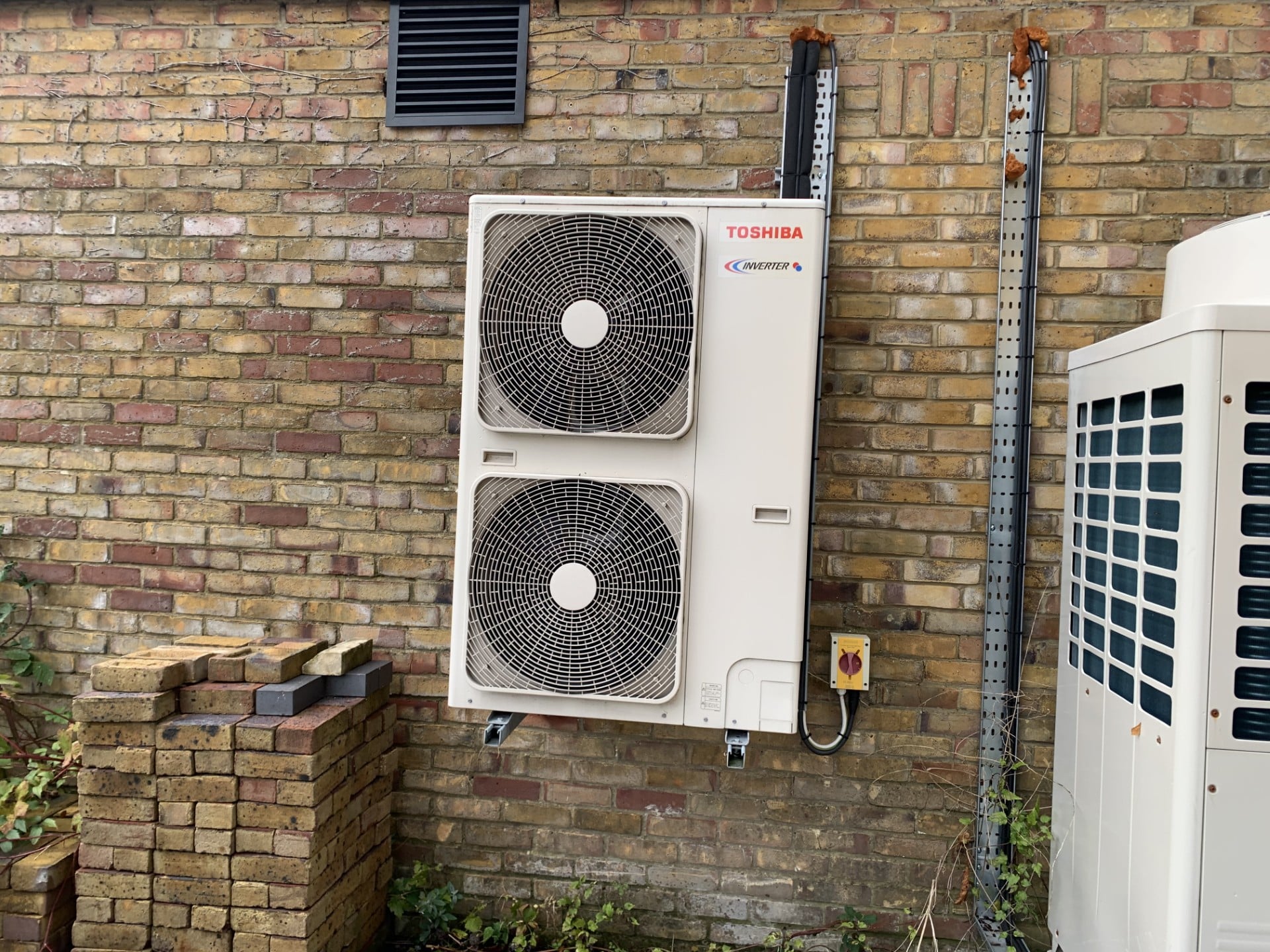
Heat decarbonisation refers to the process of transitioning from carbon-intensive heating systems (like gas or oil boilers) to low or zero-carbon alternatives. Heating accounts for a significant portion of global energy use and carbon emissions. In the UK, for instance, heating contributes to around 37% of total carbon emissions, making it one of the largest sources of pollution.
Decarbonising heat involves replacing traditional heating sources with cleaner technologies such as:
- Heat pumps: These devices extract heat from the air, ground, or water to heat homes and buildings.
- Hydrogen boilers: Hydrogen is a cleaner alternative to natural gas when used in modified boilers.
- District heating systems: These systems distribute heat from a centralised source to multiple buildings, often using waste heat from industries or renewable energy.
- Electrification: Electrifying heating systems is another solution, particularly when paired with renewable energy sources like wind or solar power.
In addition to reducing carbon emissions, decarbonising heat can improve energy efficiency and lower household energy bills. By shifting towards renewable and more efficient heating solutions, we also enhance energy security, reducing dependence on volatile fossil fuel markets.
This transformation not only supports environmental sustainability but also fosters economic growth through job creation in the clean energy sector, positioning heat decarbonisation as a crucial element in the global transition to a low-carbon future.
SAVE FOR LATER: WHY ARE HEAT PUMP INSTALLATIONS DOWN?
Why is heat decarbonisation important?
Heat decarbonisation plays a critical role in global efforts to achieve net zero emissions. For many countries, including the UK, heating is one of the most challenging sectors to decarbonise due to its deep reliance on fossil fuels.
The benefits of decarbonising heat are numerous and include:
- Reduction in greenhouse gas emissions: Transitioning to low-carbon heat sources is essential to reducing emissions from homes and buildings, which is crucial for reaching national and global climate goals.
- Energy efficiency: Many low-carbon heating technologies, such as heat pumps, are more efficient than traditional systems. This can lead to lower energy consumption and reduced energy bills over time.
- Improved air quality: Decarbonised heating systems produce fewer pollutants, helping to improve local air quality and reduce health risks associated with air pollution.
- Energy security: Moving away from imported fossil fuels towards local, renewable sources enhances energy independence and resilience against volatile fuel prices.
- Job creation and economic growth: The transition to greener heating technologies can spur innovation, create jobs in clean energy sectors, and stimulate local economies.
Heat decarbonisation as a part of net zero goals.
Achieving net zero by 2050 is a central climate goal for many nations, including the UK, as part of the Paris Agreement. Heat decarbonisation is a key component of this broader ambition, alongside other strategies like renewable energy expansion, transportation decarbonisation, and carbon capture technologies.
For the UK to hit its net zero target, the decarbonisation of heat must accelerate. According to the UK government, reaching net zero will require the decarbonisation of 29 million existing homes by 2050, alongside improvements to new builds to ensure they are energy efficient from the start.
These targets are ambitious: the UK must therefore also invest in infrastructure upgrades and scale up innovation in low-carbon technologies. Retrofitting millions of existing homes will require significant financial incentives, policy support, and public awareness campaigns to encourage adoption. In addition, building standards need to be strengthened to ensure that new developments are built with energy-efficient materials and heating systems. Collaboration between government, industry, and consumers will be critical in driving the widespread changes needed to decarbonise heat, helping to ensure a smooth and equitable transition towards a net zero future.
READ NEXT: CONSTRUCTION INDUSTRY ON TRACK FOR LESS THAN HALF OF NET ZERO GOALS
What next for decarbonisation in the UK?
The journey towards net zero is a complex but essential one. Heat decarbonisation is one of the biggest challenges, but it also offers substantial benefits for the climate, the economy, and public health. As the UK ramps up its efforts to decarbonise its heating systems, the role of governments, industries, and individuals will be crucial in turning this vision into a reality.
With the right policies, technologies, and investments, heat decarbonisation can lead to a cleaner, greener, and more sustainable future—one where net zero is not just a target but an achievable reality.
Here at Buildpass, we are fully on board with this mission. From delivering CPDs on how to achieve net zero emissions to consultancy and delivery services, we’re here to help you ensure that your next construction project ticks all of the energy efficient boxes.
Drop us a line to book your free consultation and find out more.
READ NEXT: TRENDS IN UK SUSTAINABLE CONSTRUCTION